What is Terahertz radiation
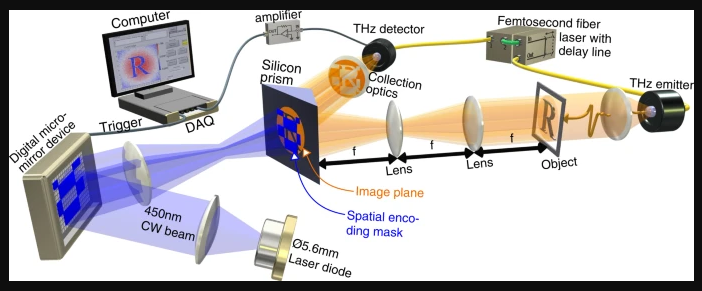
THz imaging technology
Like other imaging techniques in different spectral bands, THz imaging technology also utilizes THz rays to irradiate the object being measured, obtaining information about the sample through transmission or reflection, and then forming an image. THz imaging technology can be divided into two methods: pulsed and continuous. The former possesses the characteristics of THz time-domain spectroscopy. At the same time, it can perform functional imaging of material groups, obtaining the distribution of refractive indices within the material. For example, with a sunflower seed, it is possible to easily obtain internal information about the seed. Figures 3-4 show the physical photograph of a sunflower seed sample and the corresponding THz transmission image reconstructed using the method, which can clearly distinguish the contour of the shell and the shape of the kernel hidden inside the shell, which is highly desirable. Similarly, if the sample is a human tooth, the normal parts of the tooth and the damaged or decayed parts can be easily distinguished, and there is no additional harm to the human body as X-rays are not required.
THz radar
In essence, this is also a form of imaging. Given the strong absorption of THz rays by moisture in the atmosphere, short-range radar represents a strength of THz technology. One highly anticipated application is through-wall radar and mine detection radar, which can also be used in search and rescue operations for victims in earthquake relief efforts, although these are still in the research and development stage. This is because materials such as walls and wood allow THz rays to pass through, whereas the human body, which contains a significant amount of water, does not. Therefore, it is possible to detect the distribution and activities of individuals inside a building through the walls, which can have a profound impact on counter-terrorism and anti-kidnapping efforts. Similarly, this technology can also be used to locate individuals beneath rubble. As for mine detection radar, it is based on the fact that mines are typically located on or near the surface of the ground, and dry soil allows THz rays to pass through. The mines will reflect the THz rays back, enabling the detection of the targets.
THz Astronomy
In the universe, a significant amount of matter emits THz electromagnetic waves. Numerous molecules such as carbon (C), water (H2O), carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen (N2), and oxygen (O2) can be detected in the THz frequency band. Prior to the application of THz technology, some of these substances were completely undetectable, while others could only be detected at very high altitudes or on the surface of the moon.
THz Communication Technology
THz technology, when applied to communication, can achieve wireless transmission speeds of 10GB/s, particularly in satellite communication. In the near-vacuum state of outer space, where the influence of moisture is not a concern, this is several hundred to over a thousand times faster than current ultra-broadband technologies. This allows THz communication to conduct high-bandwidth and highly secure satellite communications. Although the lack of efficient THz transmitting antennas and sources currently prevents its commercialization in the communication sector, this challenge is bound to be addressed by the development of novel emitting devices and sources.
Terahertz radiation
German researchers, using supercomputers, have discovered that intense terahertz radiation can instantaneously boil a microscopic amount of water in less than a trillionth of a second.
Terahertz radiation refers to the electromagnetic radiation region with frequencies ranging from 0.1 terahertz to 10 terahertz, and wavelengths between millimeter waves and infrared rays. One terahertz is equal to one trillion hertz.
The Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (DESY) research center in Germany reported that intense terahertz radiation can cause water molecules to vibrate violently, breaking the hydrogen bonds between them. This method can heat approximately one nanoliter (one billionth of a liter) of water to 600 degrees Celsius within half a picosecond (one picosecond is one trillionth of a second).
The report points out that although one nanoliter of water may sound insignificant, it is sufficient for many experiments. A picosecond is much faster than the blink of an eye, so this method of boiling water can be considered the fastest to date.
Although this "water boiling" method has not yet been put into practice, researchers suggest that water plays a crucial role in many chemical and biological processes, and this new discovery may provide more experimental possibilities for the fields of chemistry and biology.
